What is the Difference Between Cable Sheathing and Cable Insulation? In electrical and industrial applications, cables play a crucial role in safely transmitting electricity and signals. While cables are designed to perform effectively under various cond
Jan 10, 2025In electrical and industrial applications, cables play a crucial role in safely transmitting electricity and signals. While cables are designed to perform effectively under various conditions, their protection is equally important. To ensure safe and reliable operation, cables are equipped with two critical protective layers: cable insulation and cable sheathing. Though they serve similar purposes in protecting the internal components of the cable, they differ in their functions, materials, and placement. Understanding the distinction between cable insulation and cable sheathing is vital for selecting the appropriate cables for specific applications.
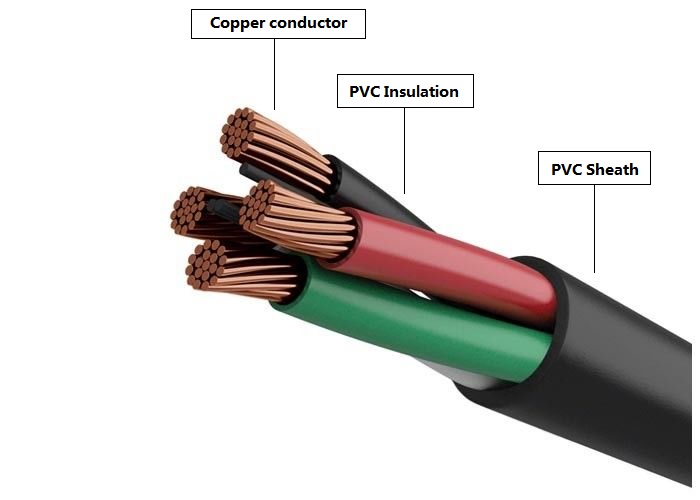
Cable insulation refers to the layer that surrounds the conductive material (usually copper or aluminum wires) within the cable. Its primary function is to prevent electrical contact between the conductors and to ensure that electricity flows smoothly through the conductors without leakage or short circuits. Insulation also provides protection against external environmental factors that could damage the wires, such as moisture, heat, and chemicals.
The material used for insulation must be an excellent electrical insulator, meaning it does not allow electrical currents to pass through it. This layer is often designed to withstand high temperatures, mechanical stress, and other conditions that could compromise the safety and performance of the cable. Common materials used for cable insulation include:
Cable sheathing refers to the outer protective layer that surrounds the entire cable assembly, including the conductors, insulation, and any additional components (like fillers or reinforcement). The primary function of cable sheathing is to provide mechanical protection, safeguard the cable from physical damage, and prevent environmental elements such as moisture, abrasion, and UV radiation from compromising the integrity of the cable.
While cable insulation is focused on electrical protection, sheathing is designed to provide physical and environmental protection. Sheathing materials are typically designed to be durable and resistant to mechanical wear, such as crushing, bending, and impacts. In some cases, sheathing materials are also designed to be fire-retardant or resistant to extreme weather conditions.
Common materials used for cable sheathing include:
While both cable insulation and cable sheathing are essential for ensuring the proper performance of cables, they differ in their purpose, materials, and placement. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
| Aspect | Cable Insulation | Cable Sheathing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents electrical leakage and ensures safety by isolating conductors. | Provides mechanical protection, safeguarding the entire cable assembly from physical damage. |
| Placement | Surrounds the individual conductors (wires). | Encapsulates the entire cable, including insulation and conductors. |
| Materials | PVC, XLPE, Rubber, Teflon, etc. | PVC, PE, Rubber, LSZH, Steel Wire Armor, etc. |
| Protection Type | Electrical isolation, protection from electrical faults and external influences (moisture, heat). | Physical protection from mechanical damage, environmental protection (UV, chemicals, moisture). |
| Temperature Resistance | Typically designed for a higher temperature range to protect conductors. | Can also be designed to resist extreme temperatures, but focuses more on physical durability. |
| Fire Resistance | May have fire-resistant properties but is mainly focused on electrical safety. | Can be designed to resist fire and minimize smoke and fume release, especially for cables used in public or industrial spaces. |
Both insulation and sheathing are vital to the longevity and functionality of cables. Insulation ensures that cables are safe to use and do not cause electrical hazards, such as short circuits or shocks. Sheathing, on the other hand, provides an additional layer of protection that helps cables resist damage from external physical forces, weather, and environmental elements.
For instance, in industrial environments where cables are exposed to heavy machinery or chemicals, the sheathing offers an extra layer of protection against abrasion and environmental factors, while the insulation ensures that the cables perform safely and efficiently under electrical load.
In other applications, such as in residential buildings, PVC insulation and sheathing are often used together to provide a safe and durable cable that meets both electrical and mechanical safety standards. Fire-resistant sheathing (like LSZH) is crucial for installations in public buildings, where human safety is a priority.
While cable insulation and sheathing may seem similar, they serve distinct purposes in maintaining the safety and reliability of electrical systems. Cable insulation is focused on electrical safety, preventing electrical faults and leakage, whereas cable sheathing is designed to provide mechanical and environmental protection to the entire cable assembly. When selecting cables for specific applications, it is important to consider both the insulation and sheathing to ensure optimal performance, safety, and durability.
At DYSen, we offer a wide range of high-quality cables that meet global standards for insulation and sheathing, ensuring your electrical systems are both safe and reliable. Visit our product page to learn more about our PVC Insulated and Sheathed Power Cables.